Footprint Libraries
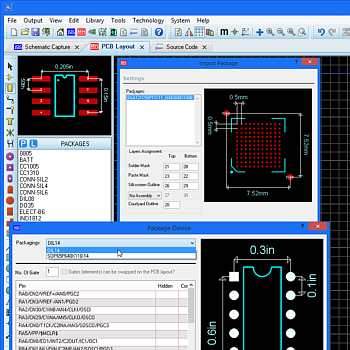


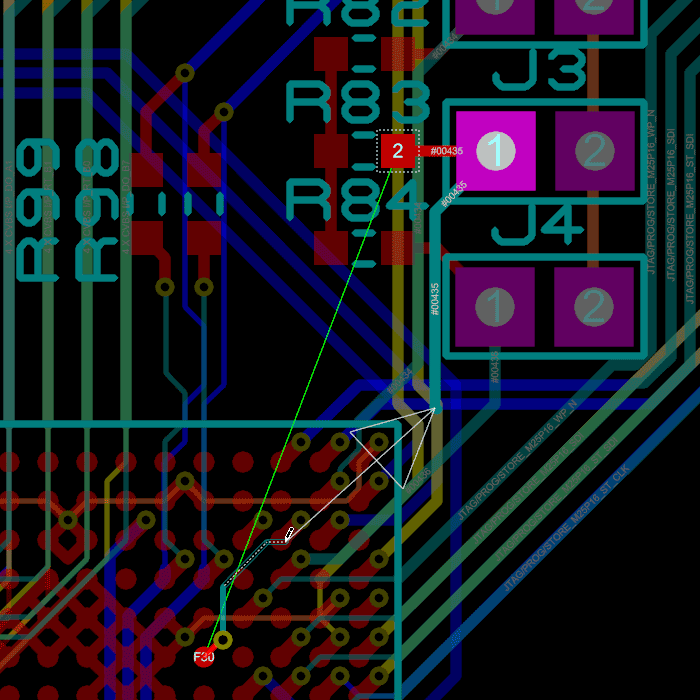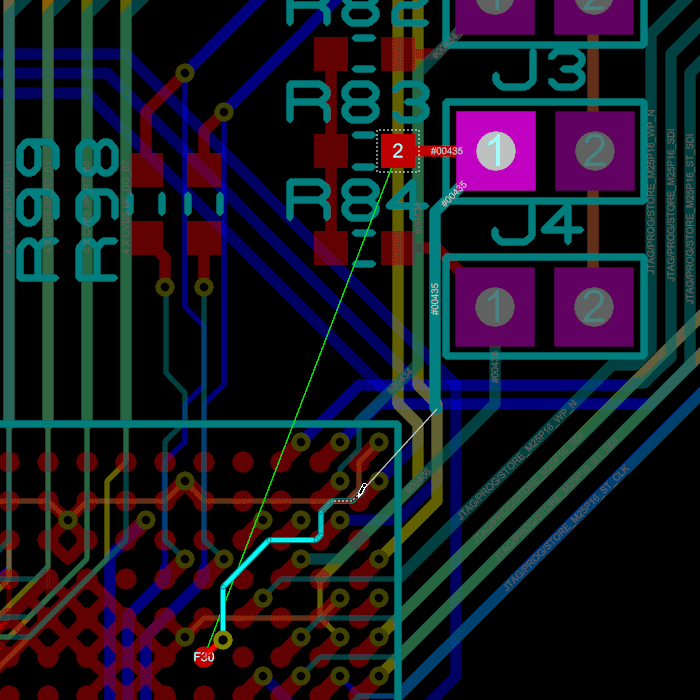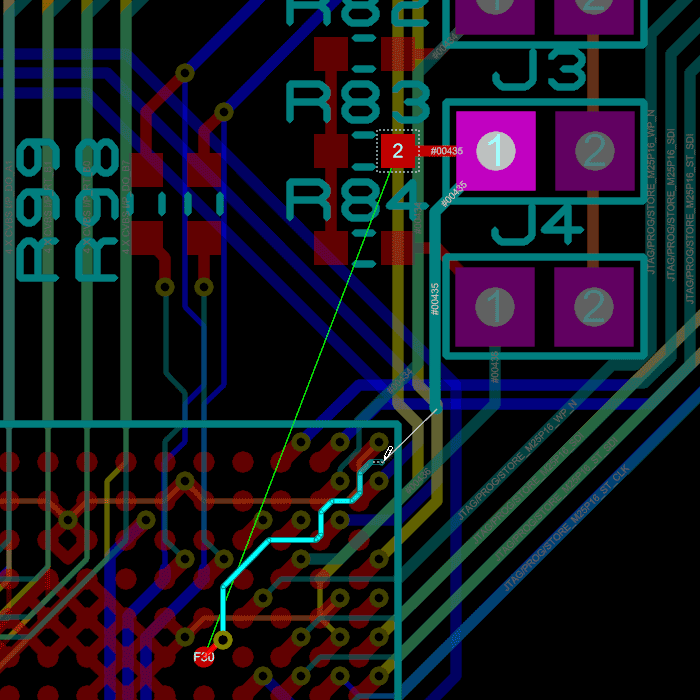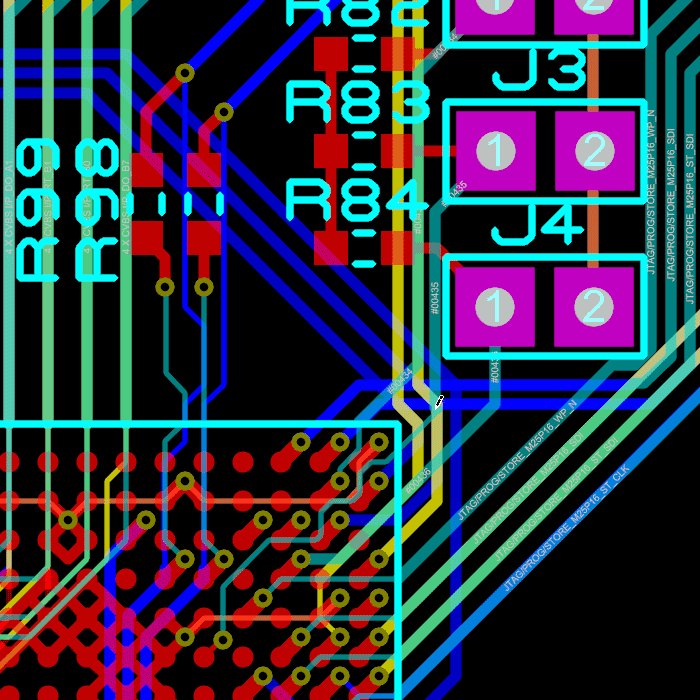
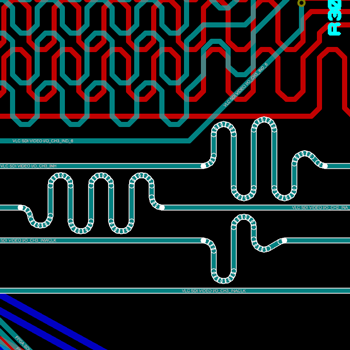
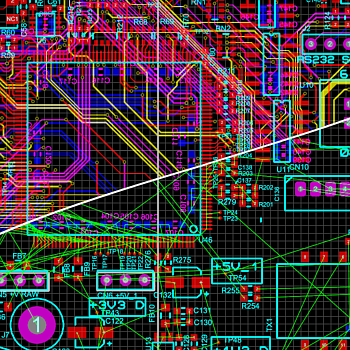

You can place a flood fill with all PCB packages but the ability to place multiple power planes per layer is part of the advanced feature set and requires Proteus PCB Design Level 2 or higher.

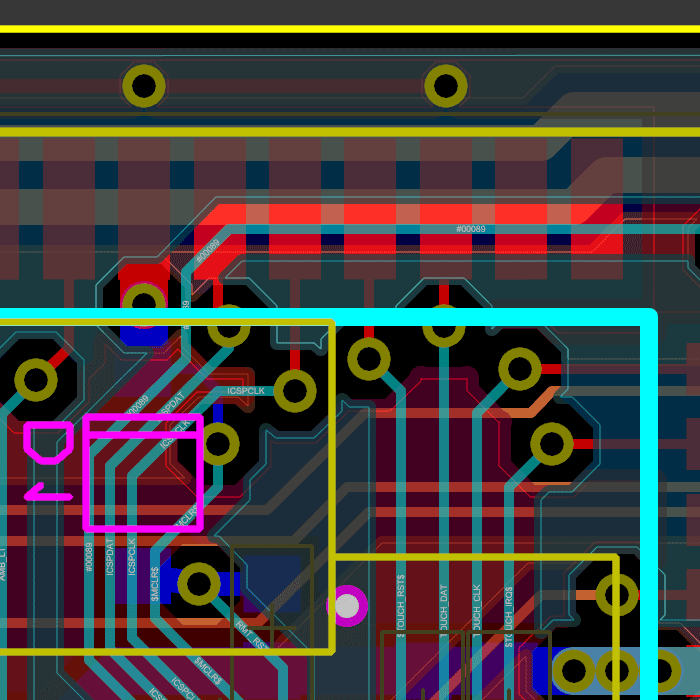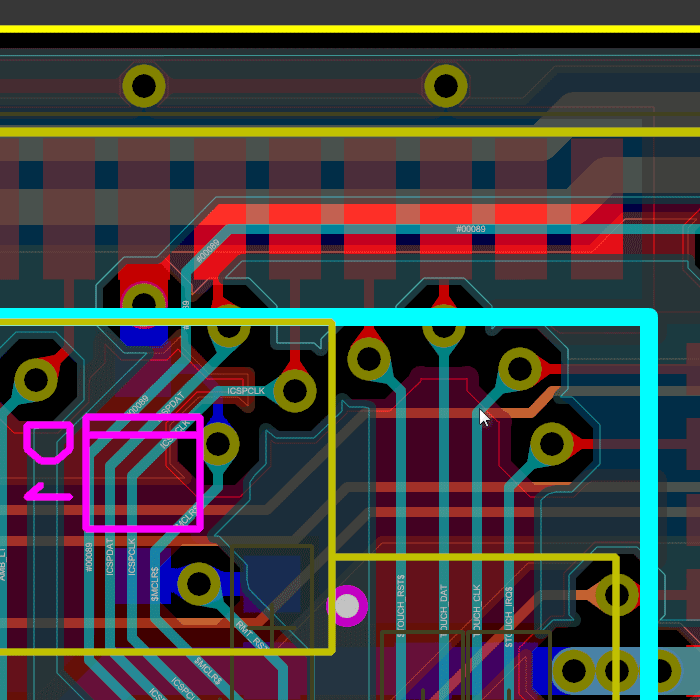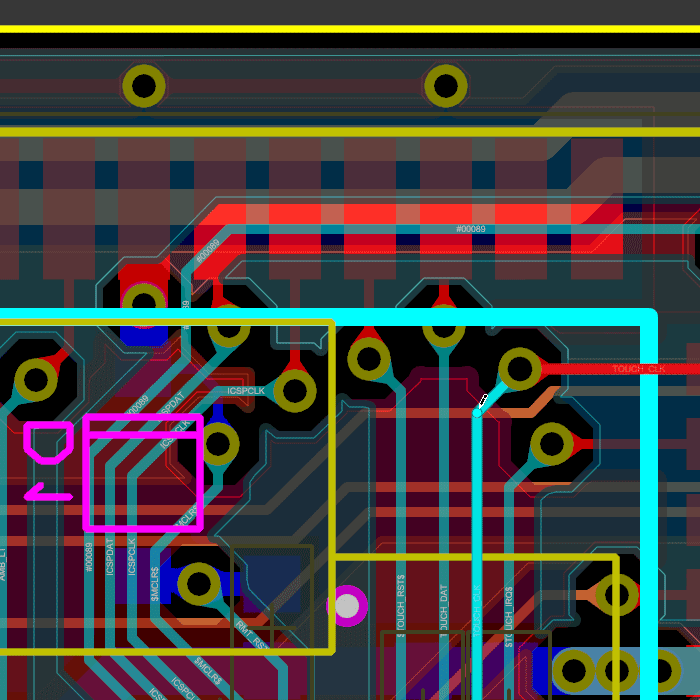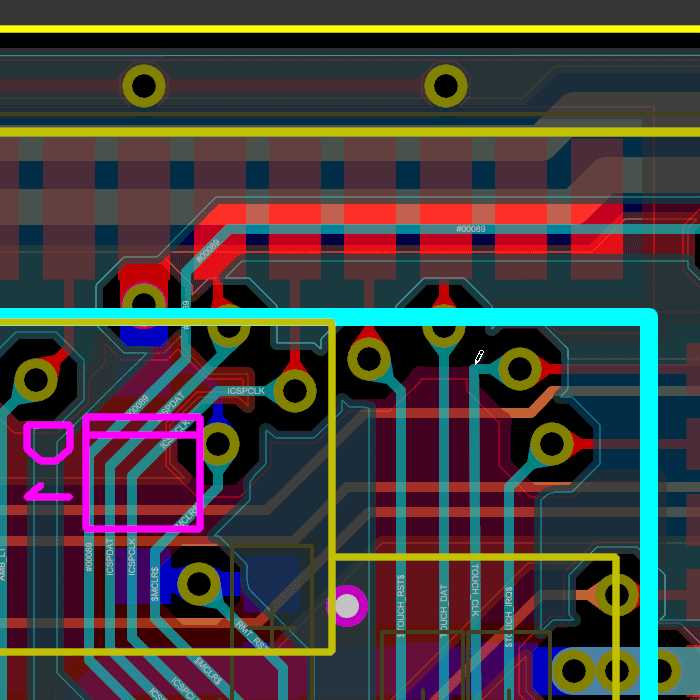
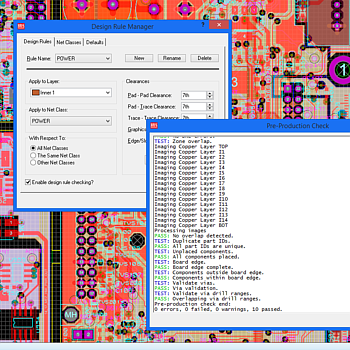
The 3D Viewer, along with its associated import and export formats is part of the Advanced Feature Set and is available only with Proteus PCB Design Level 2 and higher.

Mechanical CAD output formats such as STEP, IGES, STL and IDF along with the ODB++ advanced manufacturing format are part of the Advanced Feature Set and are limited to the Proteus PCB Design Level 2 and higher.